Newton's third law of motion – action and reaction - ppt video
4.5 (76) · € 13.00 · En Stock
4.1 A force is a part of an interaction A force is part of a mutual action – or interaction The forces always occur in pairs – called a force pair The forces are equal in strength and opposite in direction and they occur at the same time
Newton’s third law of motion – action and reaction
A force is part of a mutual action – or interaction. The forces always occur in pairs – called a force pair. The forces are equal in strength and opposite in direction and they occur at the same time.
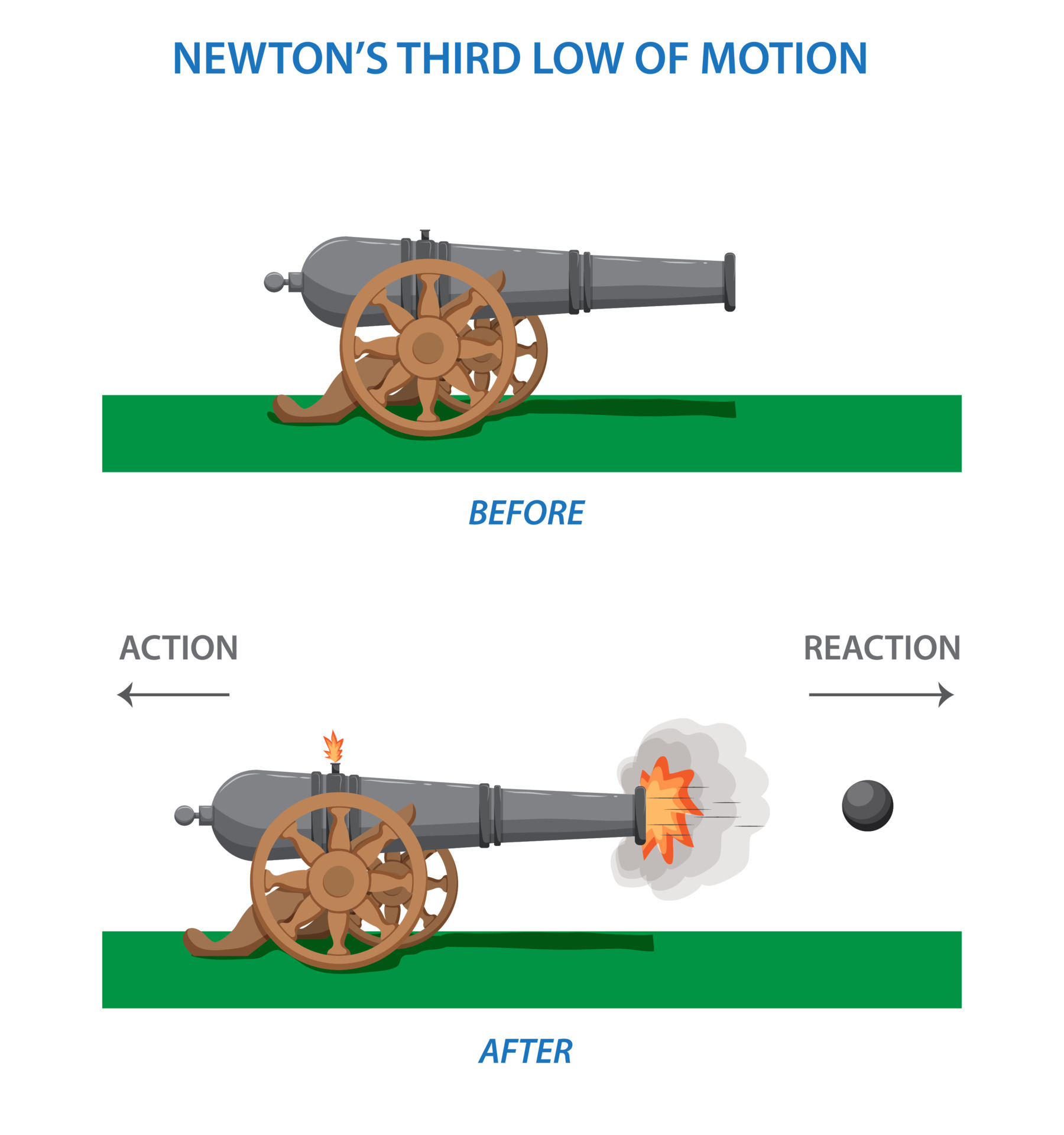
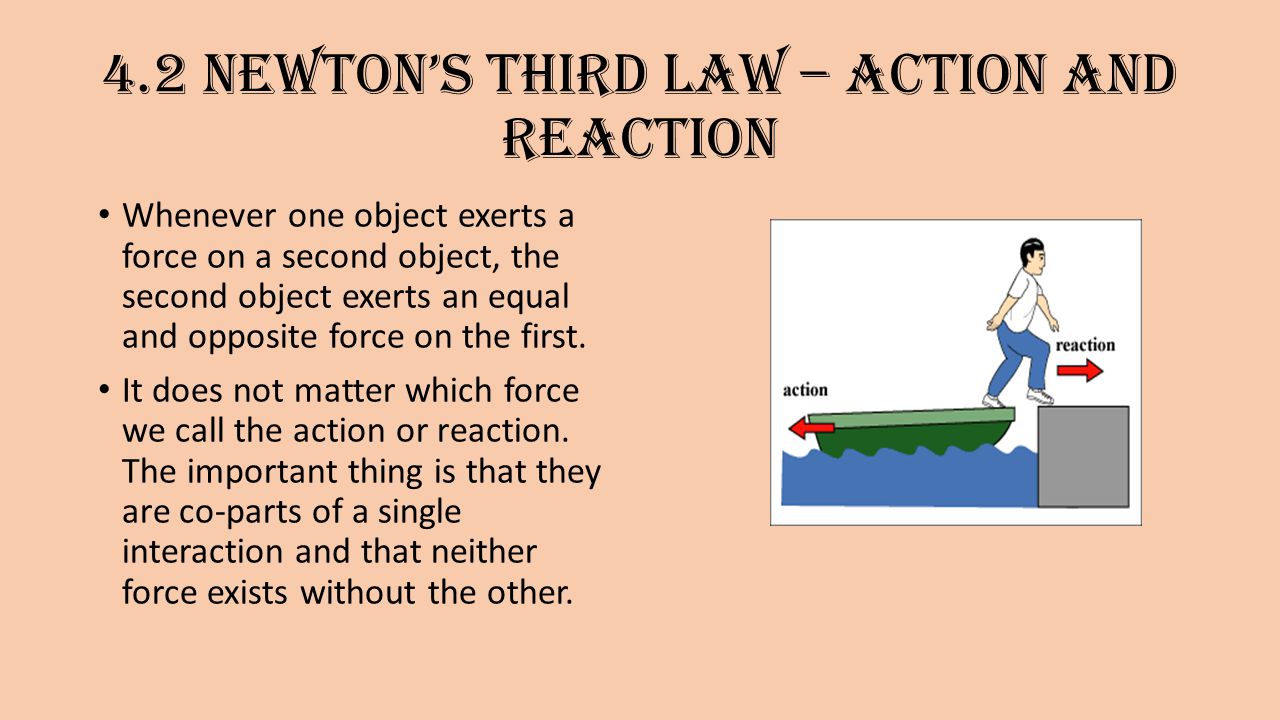
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. It does not matter which force we call the action or reaction. The important thing is that they are co-parts of a single interaction and that neither force exists without the other.
If the action is A on B, the reaction is B on A. Example: Tire pushes on road, road pushes on tire.
Remember the 2nd Law of Motion! A given force exerted on a small mass produces a large acceleration, while the same force exerted on a large mass produces a small acceleration.
Why don’t action reaction pairs cancel to zero They act on different objects! A system is a collection of objects that you are studying.
4.6 the classic horse – cart problem
Examples: Tug of war. Helicopter. Bird flying. Animal locomotion.
vocabulary Force pair Interaction Newton’s third law system
.PNG)
Newton's Laws - Presentation Physics

Lesson 3.5 - Newton's 3rd Law of Motion (Force Pairs) - Classful

Newton's third law of motion, Action and Reaction

Newton's Third Law

Newton's Third Law of Motion, Definition, Application & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript
Physics Newton's Third Law of Motion Action-Reaction, Lesson & Lab Exploration

Newton's Laws of Motion Lesson - Bright in the Middle

PPT – Newtons Third Law of Motion PowerPoint presentation

Newton's Third Law of Motion - Science Class 9 PDF Download